Introduction: why IoT connectivity matters more than ever
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries by enabling billions of devices to collect, transmit, and act on data in real time. At the core of every IoT deployment lies one critical decision: connectivity.
Two main technologies dominate: cellular IoT and satellite IoT. While cellular IoT uses terrestrial mobile networks, satellite IoT connects devices through space-based infrastructure. These approaches often complement each other, especially in hybrid IoT solutions where seamless global coverage is essential.
This guide explains the technical foundations, network types, use cases, and decision-making factors for choosing between cellular, satellite, or hybrid IoT connectivity.
Table of Contents
What is cellular IoT?
Types of cellular IoT networks
What is satellite IoT?
Types of satellite IoT networks
Key players in satellite IoT
Cellular vs satellite IoT: technical comparison
Hybrid IoT networks: the best of both worlds Industry use cases
Com4: your global IoT connectivity partner
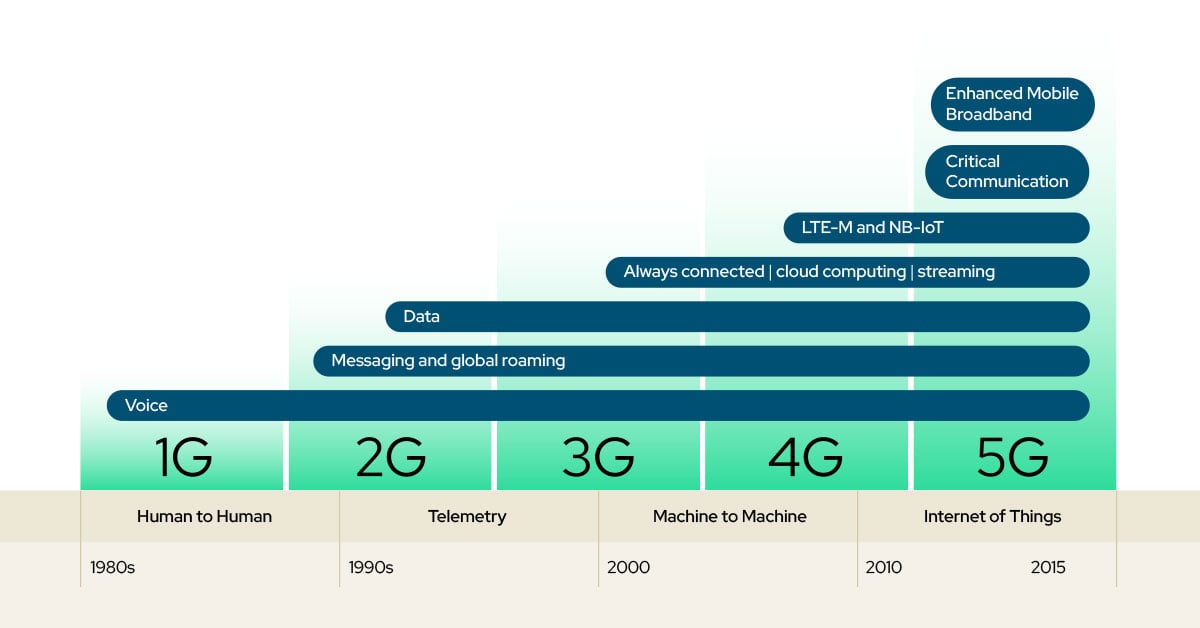
What is cellular IoT? (2G, 3G, 4G, LTE-M, NB-IoT, 5G)
Cellular IoT connects devices using mobile network infrastructure and the same licensed spectrum as smartphones. Standardized by 3GPP, it offers:
- Wide coverage in urban and suburban areas.
- Low latency for real-time applications.
- High bandwidth for data-heavy IoT devices.
- Established infrastructure with ongoing 5G rollouts.
Top use cases: industrial automation, connected healthcare, logistics tracking, smart cities, and environmental monitoring.
Types of cellular IoT networks
Legacy cellular networks
- 2G (GSM) – Low data rates for basic telemetry; being phased out globally.
- 3G (UMTS) – Moderate speeds; also facing shutdown in many regions.
- 4G LTE – High speed, low latency, robust IoT module ecosystem.
LPWAN cellular IoT
- NB-IoT – Deep building penetration, ultra-low power, small payloads.
- LTE-M – Mobility-friendly, supports VoLTE, ideal for asset tracking.
5G IoT
- 5G NR – Ultra-low latency (<10 ms), multi-Gbps speeds, network slicing.
- 5G RedCap – Balanced speed, efficiency, and cost for industrial IoT.
What is satellite IoT? (LEO, MEO, GEO)
Satellite IoT connects devices directly to satellites, bypassing terrestrial towers. This makes it ideal for remote areas, maritime operations, and critical infrastructure.
Advantages:
- Global coverage (including oceans & polar regions).
- No dependence on terrestrial infrastructure.
- Crucial for disaster recovery & mission-critical use cases.
Challenges:
- Higher latency than cellular.
- Lower bandwidth (bps–kbps typical for IoT).
- Higher hardware and service costs.
Types of satellite IoT networks
|
Orbit type |
Altitude |
Latency |
Coverage |
Example use cases |
|
LEO (Low Earth Orbit) |
160–2,000 km |
20–40 ms |
Smaller footprints; requires large constellations |
Precision agriculture, maritime tracking, broadband |
|
MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) |
2,000–35,786 km |
100–150 ms |
Larger coverage, fewer satellites |
GNSS, aviation, fleet tracking |
|
GEO (Geostationary) |
35,786 km |
240–270 ms |
Fixed wide-area coverage |
Weather, fixed assets, broadcast services |
Key players in satellite IoT
- Iridium – Global LEO network for M2M.
- Orbcomm – LEO satellites for logistics.
- Inmarsat – GEO for maritime, aviation.
- Globalstar – LEO for low-data IoT.
- Starlink – High-speed LEO broadband.
- Sateliot – LEO NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network) for direct-to-device 5G IoT.
Cellular vs satellite IoT – technical comparison
|
Factor |
Cellular IoT |
Satellite IoT |
|
Coverage |
Strong in urban/suburban |
Global, including oceans & polar |
|
Latency |
<10 ms (5G) |
20–270 ms depending on orbit |
|
Data rates |
Kbps–Gbps |
bps–Kbps |
|
Power usage |
Low (LPWAN optimized) |
Higher (longer distances) |
|
Cost |
Lower for most cases |
Higher; tied to satellite airtime |
|
Mobility |
Seamless handovers |
Variable performance |
Hybrid IoT networks: the best of both worlds
Hybrid Satellite-Terrestrial Networks (HTSN) combine both cellular and satellite links to:
- Maintain uptime in remote areas.
- Provide redundancy for mission-critical services.
- Reduce costs by using satellite only when cellular is unavailable.
5G Release-17 NTN standards now allow devices to switch seamlessly between satellite and cellular without changing hardware.
Industry use cases for cellular, satellite, and hybrid IoT
Agriculture– Soil sensors, livestock tracking (NB-IoT + LEO satellite).Energy– Remote pipeline monitoring (satellite) + grid optimization (cellular).
Maritime – Vessel tracking, real-time weather, safety beacons.
Transportation– LTE-M fleet tracking with satellite fallback.
Environmental monitoring – Forest fire detection, glacier observation.

Com4: your trusted partner for global IoT connectivity
At Com4, we provide the complete range of IoT connectivity services:
- All cellular technologies: 2G, 3G, 4G, LTE-M, NB-IoT, and 5G.
- Satellite IoT services: including LEO services.
- Official partner of Sateliot – delivering direct-to-device 5G NTN satellite IoT
- Partnership with Starlink – enabling high-speed LEO broadband for IoT
- Hybrid IoT connectivity – seamless switching between terrestrial and satellite networks.
With expert consultancy, rapid delivery, and global roaming, Com4 ensures that IoT deployments are resilient, secure, and future-ready — whether in cities, offshore, or the most remote parts of the planet.

 CASE STUDY
CASE STUDY



.png)


.jpg)
.jpg)