These technologies enable efficient, long-range connectivity for billions of devices worldwide. Understanding their unique strengths — including speed, coverage, mobility, and power usage — is critical when deciding which best suits your IoT deployment.
What is LTE-M?
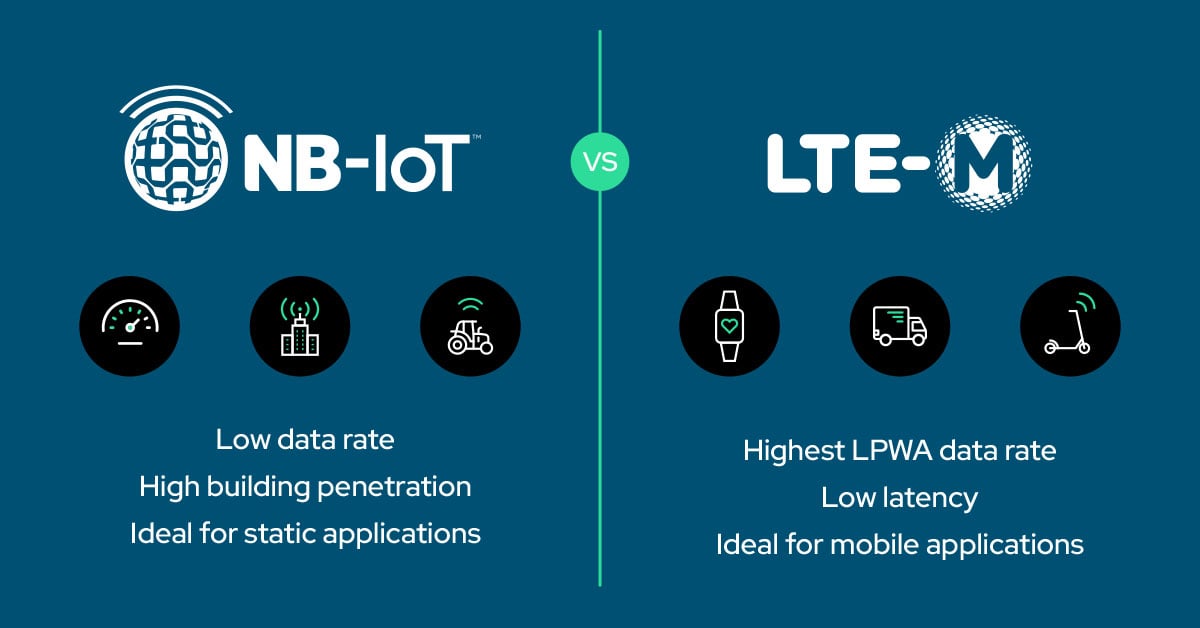
LTE-M (Long Term Evolution for Machines) is a cellular LPWA technology built on the existing 4G LTE framework that supports higher data rates, mobility, and voice features (VoLTE) while maintaining low power consumption. It operates with a 1.4 MHz bandwidth and enables devices to stay connected while moving between cells, making it suitable for applications that require consistent connectivity and frequent data exchanges.
At Com4, LTE-M has powered real-world applications such as:
- Sensorita’s smart waste management solution uses LTE-M connectivity from Com4 to enable real-time monitoring of container fill levels, ensuring reliable data transmission and efficient route optimization.
- Soundsensing’s machine noise monitoring, using Com4’s mobile network to send continuous sensing data to predictive maintenance platforms.
These implementations show how LTE-M supports mobile and moderate-data IoT use cases requiring reliable, long-term connectivity.
What is NB-IoT?
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) focuses on ultra-low power consumption and superior coverage, especially indoors and underground, using a narrow 180–200 kHz bandwidth. It’s ideal for stationary devices that send small amounts of data infrequently, such as utility meters and environmental sensors. Battery life can exceed 10 years in many deployments due to the technology’s efficiency.
Com4’s NB-IoT connectivity supports use cases such as:
- A citywide parking solution leverages NB-IoT sensors to monitor parking space availability, ensuring stable connectivity and low power consumption.
- Environmental and utility monitoring applications that benefit from NB-IoT’s deep indoor reach and energy efficiency.
These examples highlight NB-IoT’s suitability for low-data, long-life static sensor deployments.
Key Differences Between LTE-M and NB-IoT
While both LTE-M and NB-IoT are LPWA technologies standardized by 3GPP, they serve different IoT needs. LTE-M provides greater speed and mobility, whereas NB-IoT prioritizes coverage and power efficiency.
Speed & Bandwidth
- LTE-M: Higher throughput suitable for more frequent, larger data transfers.
- NB-IoT: Lower bandwidth, ideal for small and infrequent messages.
Mobility & Roaming
- LTE-M: Full mobility with handover support and broader roaming coverage.
- NB-IoT: Designed mostly for static devices, with limited roaming coverage.
Battery Life
- LTE-M: Long battery life but higher energy use under frequent communication.
- NB-IoT: Exceptional energy efficiency, often achieving 10+ years on battery.
Coverage & Penetration
- LTE-M: Reliable wide-area coverage.
- NB-IoT: Often better deep-indoor/underground penetration due to narrow bandwidth.
Device Cost & Complexity
- LTE-M: Typically higher module cost due to enhanced features.
- NB-IoT: Lower-cost and simpler modules, ideal for large-volume sensor rollouts.
LTE-M vs NB-IoT Comparison Table
|
Feature |
LTE-M |
NB-IoT |
|
Data rate |
Higher (up to ~1 Mbps) |
Lower (up to ~250 Kbps) |
|
Mobility |
Full support |
Static only |
|
Power efficiency |
High |
Very high |
|
Coverage depth |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Latency |
Low |
Higher |
|
Voice (VoLTE) |
Yes |
No |
|
Module cost |
Medium |
Low |
|
Best for |
Mobile & moderate data |
Static & low data |
Choosing the Right Network Based on Real-Life Use Cases
Selecting the best LPWA technology depends on how your IoT devices operate and the data they send. Com4’s real projects demonstrate where each technology performs best.
LTE-M is best for:
- Smart environmental monitoring networks where sensors send moderate data over long periods.
- Machine maintenance systems like Soundsensing’s noise sensors, transmitting continuous data for predictive insights.
- Connected logistics & fleet systems requiring roaming and mobility across regions.
- Industrial IoT sensors that need regular updates and moderate data throughput.
NB-IoT is best for:
- Stationary environmental and utility meters with low data requirements.
- Smart building sensors that report status infrequently over long battery life.
- Networked environmental monitoring systems using NB-IoT’s deep penetration.
- Long-term sensor deployments in infrastructure where deep indoor coverage matters.
- Static health or safety monitors requiring ultra-low-power connectivity.
Which One to Pick: LTE-M or NB-IoT?
Here’s a quick checklist to help you choose:
|
Requirement |
Better Option |
|
Mobility |
LTE-M |
|
Deep indoor coverage |
NB-IoT |
|
High data volume |
LTE-M |
|
Maximum battery life |
NB-IoT |
|
Voice support |
LTE-M |
|
Lowest cost modules |
NB-IoT |
|
Real-time data |
LTE-M |
|
Static deployments |
NB-IoT |
Real-World Deployment Challenges
Even mature LPWA technologies require careful planning:
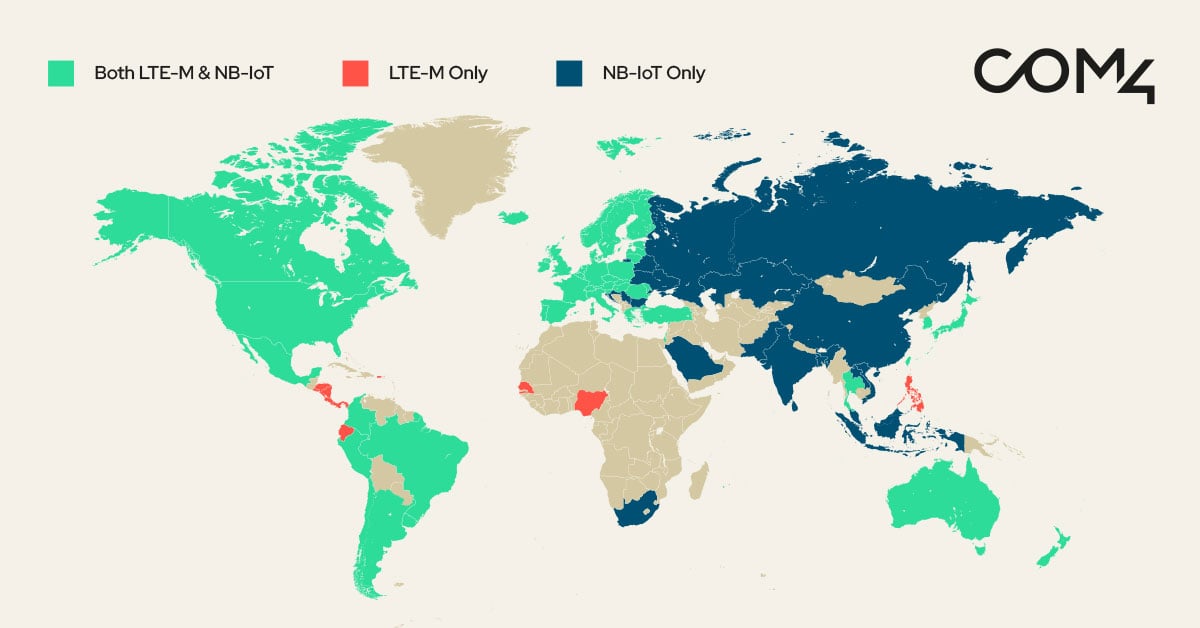
- NB-IoT roaming remains limited in some regions, while LTE-M offers broader roaming agreements.
- Coverage can vary due to operator spectrum strategies.
- Device certification and module compatibility differ between vendors.
- Migrating from legacy 2G/3G systems may require hybrid strategies.
How Com4 Supports Your IoT Connectivity
At Com4, we deliver Managed IoT Connectivity that integrates LTE-M, NB-IoT, 4G, 5G, and satellite connectivity into a unified solution with eSIM and iSIM technology and carrier-agnostic SIM cards connecting to 750+ networks across 190+ countries. Our connectivity underpins projects like MedThings’ connected medication dispensers, which use Com4 eSIM for secure, real-time healthcare data transmission, and Intellity’s construction security cameras, which rely on reliable mobile connectivity to prevent theft and vandalism across job sites.
As 2G and 3G networks sunset globally, LTE-M and NB-IoT are foundational technologies for the next phase of IoT growth. Standardized by 3GPP and adopted by hundreds of networks worldwide, these technologies enable billions of devices to communicate efficiently. LTE-M excels in mobility and data usage, while NB-IoT is ideal for static, low-power deployments. Understanding their differences — supported by real Com4 IoT use cases — helps ensure your project delivers performance, scalability, and cost effectiveness.
FAQs About NB-IoT and LTE-M Connectivity
Can one device support both LTE-M and NB-IoT at the same time?
How do 2G/3G network shutdowns affect NB-IoT and LTE-M deployments?
They don’t - both LTE-M and NB-IoT are part of the 4G/5G IoT ecosystem designed to replace legacy standards.
Does LTE-M or NB-IoT work without a SIM card?
Both require SIM-based authentication, though technologies like Com4’s eSIM/iSIM allow remote provisioning without physical SIM swaps.
Will 5G replace LTE-M or NB-IoT?
No. LTE-M and NB-IoT are part of the 5G Massive IoT standard and will continue to coexist alongside 5G technology

 CASE STUDY
CASE STUDY
.jpeg?width=720&height=720&name=NB-vs-LTE-hero%20(2).jpeg)




.jpg)

